

Lupus
What is lupus?
Lupus is a long-term disease that can affect any area of the body. As an autoimmune disease, Lupus causes your immune system to attack healthy tissue in the body, resulting in pain, widespread inflammation, and tissue damage. Lupus affects many different systems of the body, including the skin, blood vessels, joints, lungs, heart, and kidneys.
What causes lupus?
While scientists do not know exactly what causes Lupus, it’s thought that it occurs in response to a combination of factors. Lupus disease has a genetic basis since the condition runs in families. It is also thought that Lupus develops in response to hormone levels, such as increased estrogen levels. Environmental factors linked to Lupus include emotional stress, infections, smoking, and exposure to silica dust.
REQUEST NOWTypes of lupus
There are four different types of the Lupus disease:
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): This is the most common type of Lupus, affecting more than 70% of people with the disease. Systemic Lupus gets its name from the fact that it affects multiple organ systems throughout the body, including the skin, joints, and kidneys.
Cutaneous Lupus: This type of Lupus only affects the skin and is worsened by exposure to sunlight. Cutaneous Lupus is characterized by rashes or lesions on the skin, especially the face, ears, neck, and legs.
Drug-induced Lupus: Drug-induced Lupus occurs when you develop Lupus symptoms after taking certain medications. The most common prescription drugs that increase your risk of drug-induced Lupus are hydralazine (treats high blood pressure), procainamide (treats irregular heartbeat), and isoniazid (treats tuberculosis). This type of Lupus is only temporary, and your symptoms will gradually disappear once you stop taking the medication.
Neonatal Lupus: This type affects babies of women who have systemic Lupus erythematosus. At birth, babies with neonatal Lupus may have a skin rash or low blood cell counts. These issues usually disappear within six months, but neonatal Lupus can cause a dangerous condition called congenital heart block in rare cases.
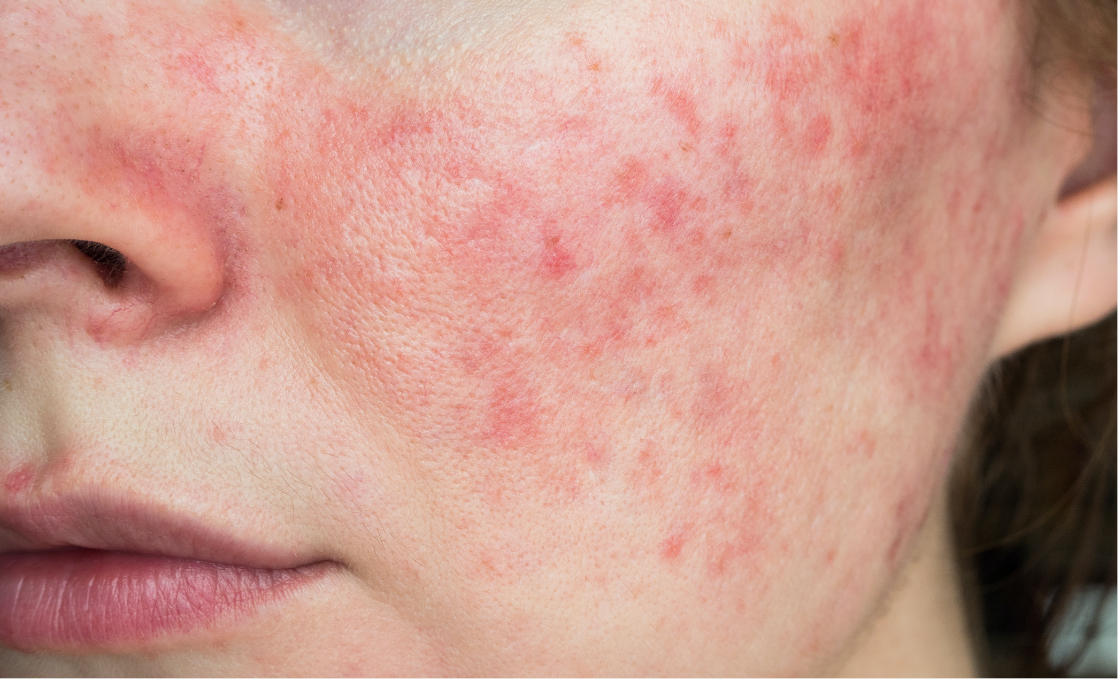
Identifying lupus symptoms
Although the disease affects everyone differently, there are Lupus symptoms that commonly occur. These include:
- A reddish, butterfly-shaped rash that forms across the cheeks and nose. Rashes can also appear on other parts of the body that are exposed to the sun, including your shoulders, arms, hands, and face.
- Fatigue
- Joint pain and swelling
- Fever
- Chest pain
- Dry eyes
How is lupus diagnosed?
Now that you know about the different types of Lupus, its causes, and symptoms, you might be wondering, “How is Lupus diagnosed?” Unfortunately, Lupus is difficult to diagnose because it produces symptoms that often overlap with many other conditions.
Your doctor will conduct a variety of tests to diagnose Lupus. You can expect your doctor to perform a complete physical examination and medical history. Blood tests are performed to identify certain antibodies, and your doctor may also take a biopsy of the skin or kidneys to see if the sample shows signs of autoimmune disease.
Lupus treatment options
Once you are diagnosed with Lupus, your doctor will provide you with Lupus facts and information regarding your Lupus treatment plan. There is not a cure for Lupus, but treatment is designed to help you prevent flares, and control and manage your symptoms.
These are some of the medications that are prescribed to control Lupus:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Taking over-the-counter NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can reduce pain and swelling.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids work by calming the immune system, which can reduce inflammation.
- Antimalarial drugs: These drugs can be used alone or with other medications to reduce skin rashes, joint pain, and fatigue.
- Biologics: Biologics are administered intravenously and can improve the symptoms of Lupus.
- Immunosuppressants: These medications are prescribed for advanced cases of lupus, especially if your central nervous system or kidneys are affected.
Along with these medications for Lupus treatment, it is important to get regular exercise to keep your bones strong, focus on eating a healthy diet consisting of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, and avoid smoking. You should also see your doctor regularly and practice sun safety by wearing a broad-spectrum sunscreen of at least 55 and protecting your skin from the sun by wearing long pants, a long-sleeved shirt, and a hat.
Interested in Lupus? Request a consultation with a skin specialist today.
*Treatment options may vary at each location.Please confirm your desired treatment is offered at your preferred location when scheduling. *Age Restriction.
For patients scheduling who are under 18 years of age (19 in Alabama and Nebraska) please make sure you have permission from your parent or legal guardian to schedule this appointment. Your parent or legal guardian must accompany you on your initial visit and on certain subsequent visits to provide appropriate informed consent.