Accidents can happen at any time. Are you prepared to treat a wound when the time comes? Below are guidelines for minor cuts and scrapes. We recommend evaluating the situation as it arises and using your best judgment to know if the wound requires immediate help through emergent care.
Step 1: Wash your hands to avoid spreading an infection to the wound.
Step 2: Stop the bleeding. Minor cuts usually stop bleeding on their own. If the bleeding does not stop on its own, apply gentle pressure with a clean bandage or cloth and elevate the wound until it stops.
Step 3: Rinse the wound with water after the bleeding has stopped. Wash around the wound with soap, but do not get soap in the wound. If you notice any dirt or debris, remove it with a tweezer cleaned with alcohol first.
Step 4: After cleaning the wound, apply an antibiotic or petroleum jelly to keep the surface moist and help prevent scarring. Certain ingredients in some ointments can cause a mild rash in some people. If a rash appears, stop using the ointment.
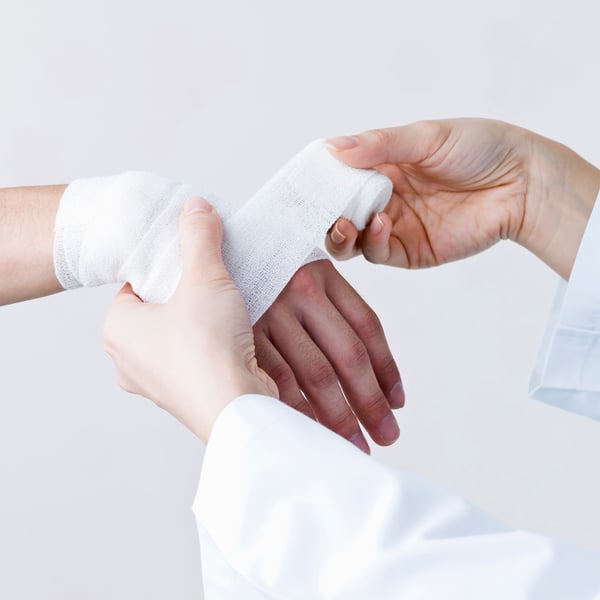
Step 5: Apply a bandage, rolled gauze, or gauze to the wound and hold it in place with paper tape. Covering the wound will keep it clean and prevent further infection.
Step 6: Change the dressing at least once a day or whenever the bandage becomes dirty or wet. While changing the bandage, watch for signs of infection, including increased redness or pain, drainage, warmth, or swelling.
If you notice an infection, contact your local board-certified dermatologist to be evaluated.